
Form the epithelium lining the ventricles and central canal of the spinal cord.Neuroepithelial cells ( neuroectoderm ).Įpendymal cells ( ependymocytes) and choroid epithelial cells Target cells for the HIV-1 virus: Infected cells fuse to form multinucleated giant cells, which are the most specific histological marker o f HIV encephalitis and HIV-associated dementia.Release inflammatory mediators (e.g., nitric oxide) and signaling molecules (e.g., glutamate).Proliferate and migrate to damaged CNS to remove cellular debris.Activated in response to CNS tissue damage.Foot processes form part of the blood-brain barrier and the glial-limiting membrane.Reactive gliosis → form of astroglial scars.Proliferate and become hypertrophic after CNS injury.

Contain bundles of intermediate filaments composed of glial fibrillary acidic protein ( GFAP an astrocyte marker).Provide physical support (scaffolding of the CNS).Radial glial cells from neuroepithelium ( neuroectoderm ).Contain spines that increase the number of synapses to other neurons.Branching, thin projections from the cell body of neurons that receive input from neighboring neurons and transmit it to the cell body.Neurofilament protein is used as a marker for neuronal cells.Most abundant in axons and the proximal part of dendrites.Microtubules with associated motor proteins for rapid axonal transport.Lacks a regular rough endoplasmic reticulum and thus does not contain Nissl substance.Connected to the cell body at the axon hillock, which is a trigger zone for initiation of action potentials, and ends in a synapse.Axon: the projection from a neuron' s cell body along which action potentials travel to send intercellular signals.Nissl staining positive in the cell body and dendrites, which have Nissl substance (aggregates of rough endoplasmic reticulum with bound polysomes).Composed of soma (cell body), axon and dendrites.Classified into unipolar, pseudounipolar, bipolar, and multipolar depending on the number of protoplasmic processes (neurites).Polarized, signal-transmitting cells that comprise the central and peripheral nervous system.Peripheral nervous system : consists of the nerves and ganglia outside the brain and spinal cord, including the cranial nerves, spinal nerves, and their roots, peripheral nerves, and neuromuscular junctions.Central nervous system ( CNS ): consists of the brain and spinal cord.The nervous system is divided into two main components:.Nerve tissue is the main tissue component of the nervous system and is primarily composed of neurons and supporting glial cells.Alterations in neurotransmitter levels have been observed in various neurological diseases, including Parkinson disease (decreased dopamine), schizophrenia (increased dopamine), depression (decreased dopamine, norepinephrine, and serotonin), and Alzheimer disease (decreased acetylcholine). Electrical synaptic transmission is the transfer of electrical signals through gap junctions. acetylcholine, dopamine, norepinephrine) from presynaptic terminals to postsynaptic receptors. Chemical synaptic transmission is the transfer of signals through the release of neurotransmitters (e.g. Synaptic transmission can be chemical or electrical. Neurons communicate through the transmission of action potentials across junctions between them called synapses.
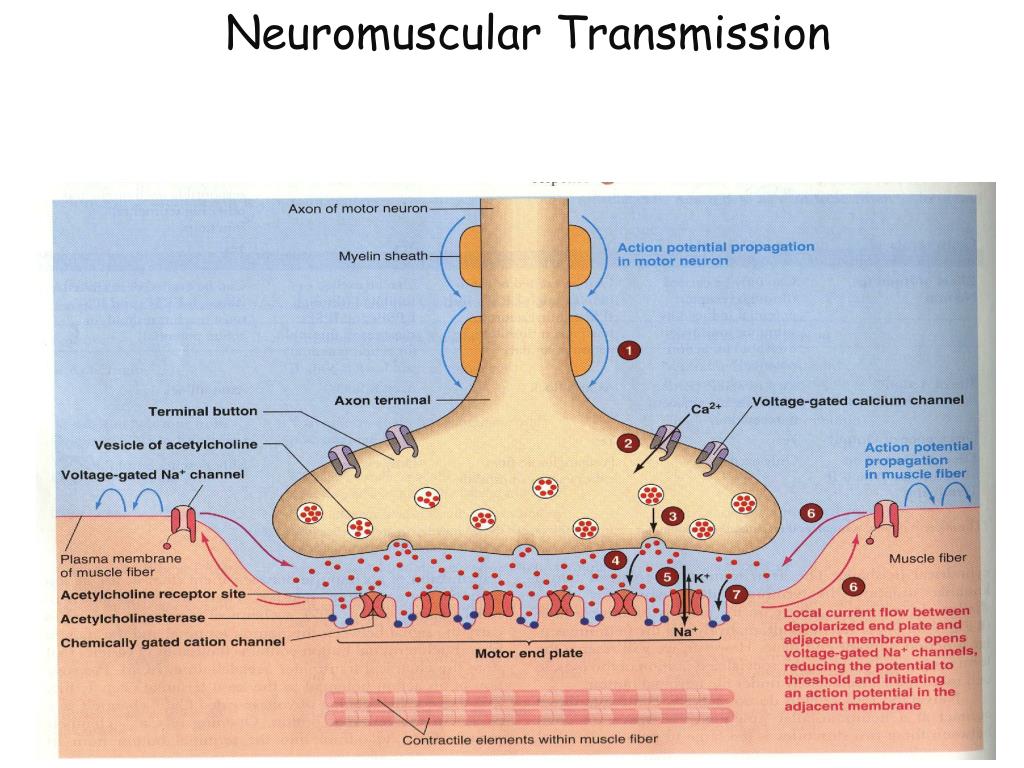
Based on their conduction velocity, diameter, and myelination, nerve fibers ( axons) are classified into large, myelinated fibers with fast conduction velocity ( group A) small, myelinated fibers with slow conduction velocity ( group B) and small, unmyelinated fibers with slow conduction velocity ( group C). Neurons are composed of dendrites, cell bodies, axons, and axon terminals. Inflammation and loss of the myelin sheath are the underlying pathologic processes in multiple sclerosis ( CNS) and Guillain barre syndrome ( PNS). Myelin sheaths increase the conduction velocity of signals across axons. Oligodendrocytes myelinate neurons in the central nervous system ( CNS), while Schwann cells myelinate neurons in the peripheral nervous system ( PNS). Nerve tissue consists of neurons, which are excitable cells that transmit information as electrical signals, and glial cells (e.g., oligodendrocytes, Schwann cells, astrocytes, microglial cells), which perform a variety of nonsignaling functions such as forming myelin to provide support and insulation between neurons, phagocytosing and removing cellular debris, removing excess neurotransmitters, and forming the blood-brain barrier.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
